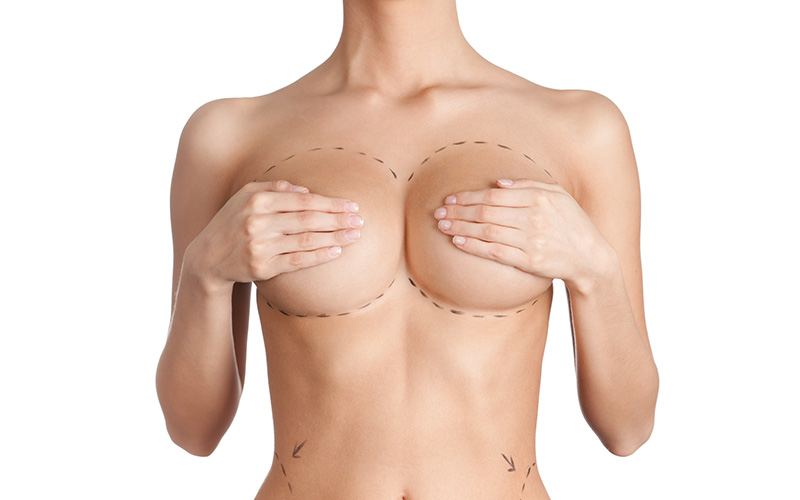
Breast Augmentation
Breast Augmentation is among the most popular aesthetic procedures of plastic surgery due to the fact that a beautiful and well-shaped breast is a universal symbol of femininity.
All the more women are deciding to undertake breast augmentation surgery in order to boost their self-esteem and improve their body image.
The procedure can be performed after a general analysis of the body and depending on the needs of each case.
Technique
There are several techniques and a wide range of implants for the surgeon and patient to choose from. Women considering a breast augmentation are advised to proceed to a mammogram and a breast ultrasound pre-operatively, as a reference for any future use.
The implant is placed in accordance with each surgical technique chosen: either under the breast (inframammary), under the arm (transaxillary) or around the areola (periareolar).
The most popular technique is called subfascial, wherevy the implant is placed below the fascia and above the pectoral muscle. This technique augments the thin membrane that covers the muscle and is called fascia, by creating a pocket where the implant is inserted thus producing a very natural result. Among its advantages is also the fact that this technique produces much fewer complications than those that may statistically occur from the operation. At the same time, it provides natural results due to the fact that the implants are practically invisible and do not cause any folds on the upper part of the breast.
On the other hand, the Dual Plane technique is highly recommended to patients with relatively small or atrophic and saggy breasts; this time, the implant is placed under the pectoral muscle up top and below the breast tissue on the bottom.
Implant Selection
Today, there are a wide variety of implants available. However, we should take into consideration that not every implant is suitable for each case, but there is an ideal implant for every woman. Implants are filled either with silicone gel or saline or their combination. Silicone can be more or less cohesive. Another difference is that they can be categorized as textured or smooth, with the first gaining field for obvious reasons. These implants carry a significant lower rate and risk of capsular contracture and they can be classified as soft and anatomical, with the latter having a more natural looking result.
The implant type that might be the best choice for a woman’s individual needs is defined by the plastic surgeon in cooperation with each patient. Also, during consultation the plastic surgeon will use measurements of both the breasts and body to determine the maximum width and projection of the breast implant that fits the patient’s proportions, as breasts do not stand alone but are an integral part of the body.
What to expect after surgery:
- During the first 24-48 hours post-operatively, it is not uncommon to feel pain and itchiness.
- The use of a surgical bra is required in order to stabilize the implants and provide adequate support.
- Strenuous exercise and activities are restricted for about 10-15 days postoperatively. During the second postoperative week, however, you may return to your everyday activities.
- After healing, the incision scars will look like barely-visible, thin lines.
Risks and Side Effects
There are usually no complications following breast augmentation surgery. In rare cases, local complications and adverse outcomes are associated with breast implant capsular contracture, which eventually leads to their removal and re-augmentation surgery, or –even rarely- implant rupture, a few weeks after surgery. In that latter case, the implant has to be removed and replaced in a few months’ time.
More rarely, the body might reject the implant within the first few weeks postoperatively. In that case also, the implant has to be removed and replaced in a few months’ time.
Major weight gain/loss or pregnancy are other factors associated with radical body changes in the body shape that may eventually lead to the need for new implants, as the existing ones may not fit anymore. For that purpose, the patient should always follow doctor’s recommendations of postoperative care; wearing a surgical bra for the first 6 months following surgery and then wearing a soft cup bra - which is the best way to hold the breasts in place.
Useful Information
- With new implant technology, the chances of capsule formation and postoperative complications are very low. The results are more natural and the breasts are stable.
- Breast augmentation procedure can be performed even during the summer months.
- Although breast augmentation procedure does not affect the ability to breastfeed, however women should be aware that they might not be able to do so. The same goes for the possible changes in nipple sensation.
- Women with implants are able to have screening mammograms, but it is important that they consult their doctor in advance.
- In a survey conducted by the Senologic Hellenic Society, 62% of men stated that female breasts are the object of sexual desire and that women’s breasts are the first thing they look at on a woman.